When we work with one item we required to use one variable, if you want work with more than one item, we can go for Arrays in Excel VBA. Arrays are the variables which allow us to store more than one value.
VBA Arrays Excel – Explained in this topic:
- What is an Array?
- What are the different types of arrays?
- One Dimensional Array:
- Multi-Dimensional (Two Dimensional) Arrays:
- How to Re-size an Array
- Array Options
- Example File
What is an Array?
Arrays are variables that allow us to store more than value in a single variable. We can refer to a specific element in the array by using the array name and an index number. Each value in the array is called an element. Since an array variable has multiple elements in it, you need a way to pick them out or reference them individually.You can do that by using a number called an index. Most of the time, the first element of an array is index number 0. Note, Array index start from 0 by default, you can change this by using Option Base , we will discuss later in this topic.
For example, we can define an array of size 7 to store 7 string type values. If you name the array as ArrayWeek to store 7 days of the week in this array, you can refer to the first element of the array as ArrayWeek(0), the second element as ArrayWeek(1), and so on, up to the last element ArrayWeek(6).
Sub sbArrayExample1()
'Dynamic array: You can define a dynamic array as follows:
Dim ArrayWeek() As Variant
'You can Store the values in the array as follows:
ArrayWeek = Array("Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat", "Sun")
'OR
'Static array: You can define with size as follows and store the values
'
' Dim ArrayWeek(7) As String
'
'
' ArrayWeek(0) = "Mon"
' ArrayWeek(1) = "Tue"
' ArrayWeek(2) = "Wed"
' ArrayWeek(3) = "Thu"
' ArrayWeek(4) = "Fri"
' ArrayWeek(5) = "Sat"
' ArrayWeek(6) = "Sun"
'You read the values from array as follows:
MsgBox ArrayWeek(0) ' It returns "Mon"
End Sub
What are the different types of arrays?
VBA gives us two flavors of array:
Static Array: The number of elements in the array, called the length of the array, is decided in advance and remains fixed.
Example: Dim ArrayWeek(7) As String
Dynamic Array: The length of the array is variable and not decided in advance.
Example: Dim ArrayWeek() As Variant
And we can have arrays with different dimensions, one dimensional array, two dimensional array or even a multidimensional array (up to 60).
One Dimensional Array:
Syntax: Dim arrayName(index) as dataType
or
Dim arrayName(first index to last index) as dataType
For example,
Dim ArrayWeek(10) as String
Dim ArrayWeek(1 to 10) as String
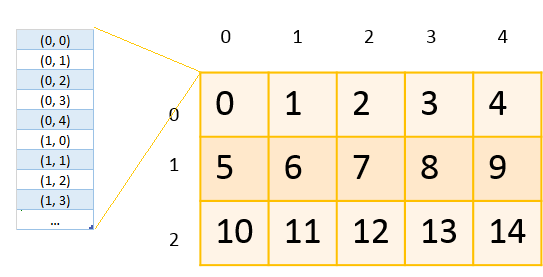
Two Dimensional Arrays:
Syntax: Dim arrayName (num1, num2) As Datatype ‘ here you can store num1*num2 items
For example,
Dim ArrayFinalData(10,20) as String ‘ here you can store 10*20=200 items
How to Re-size an Array
What if you want to add more or less items than expected, you can redefine the size of an array using ReDim Statement.
Sub sbResizeArray() Dim myarr() As String 'You thought you are required to store 5 elements, and re-sized it by Using ReDim statement ReDim myarr(2) 'stored some values myarr(0) = "Item 1" myarr(1) = "Item 2" 'But you realized you are required to store 5 more elements, re-sized to store 10 elements 'ReDim myarr(5) 'It will erase all the values alredy stored in this array to avoid that you can use Preserve statement 'Instead of the above statement use the the following to keep already stored data ReDim Preserve myarr(5) 'store the remaing items myarr(2) = "Item 3" myarr(3) = "Item 4" myarr(4) = "Item 5" MsgBox "All stored Items: " & myarr(0) & ", " & myarr(1) & ", " & myarr(2) & ", " & myarr(3) & ", " & myarr(4) End Sub
Array Options
How do you know if a variable is an array? VBA provides a handy little function (IsArray) to
test a variable.
Syntax: IsArray(Array Name) ‘ returns TRUE or FALSE
How do you Find Lower and Upper Limits of an Array?
LBound(Array Name,1) ‘ Lower bound of the first dimension
UBound(Array Name,1) ‘ Upper bound of the first dimension
LBound(Array Name,2) ‘ Lower bound of the second dimension
UBound(Array Name,2) ‘ Upper bound of the second dimension
‘Example if you define the the array as follows
Dim ArrayFinalData(10, 20) As Integer
LBound(ArrayFinalData,1) ‘Returns 0
UBound(ArrayFinalData,1) ‘Returns 10
LBound(ArrayFinalData,2) ‘Returns 0
UBound(ArrayFinalData,2) ‘Returns 20
Syntax: Erase(ArrayAname)
Ex: Erase (ArrayFinalData)
Arrays in Excel VBA – Example File to Download
You can download this file to see the vba examples on this topic.




Just a minor error spotted, the examples for Static and Dynamic arrays are mixed up.
Thanks Anuraag, we corrected it!
Dim ArrayFinalData(10,20) as String ‘ here you can store 10*20=200 items
idx start at 0 also in dynamic arr ? uphere is correct only when OPTION BASE 1 is declared ? 11*21